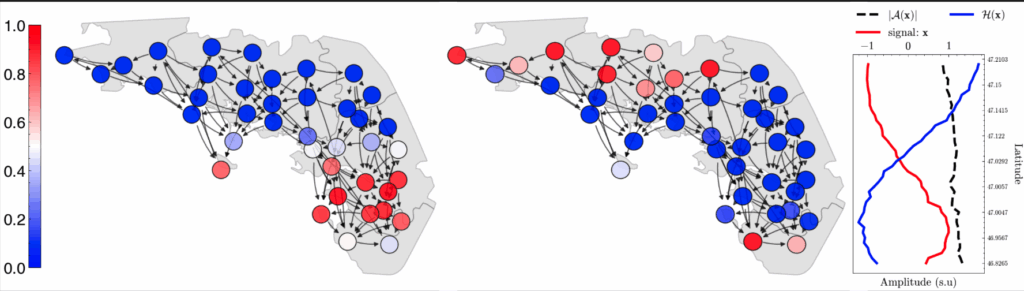
Background
For many years, wide variety of clustering methods have been employed in neuroimaging, revealing crucial network-wide patterns. Instances of such work include, functional networks (e.g Default Mode Network) and functional parcellations on resting state and task. Yet the most popular clustering methods heavily rely on either clustering distance matrices (symmetric relationship) or disentangling signal mixtures (e.g ICA). In this work we explore instead clusterings by leveraging newly introduced concepts on directed graphs dissociating from generally symmetric relationships. Contact us for more details.
Project description
This is a semester project. It is predominantly computational with a strong link with cognitive neuroscience.
Requirements
- The applicants are expected to have knowledge of signal processing.
- Good programming skills is required. Python is preferred but at least being comfortable in one programming language is required.
- Desired: Travel to Geneva 1 day per week.
Please contact Michael Chan (chunheimichael.chan@epfl.ch) with your CV and we’ll get back to you with more details about this project.
References
- C. H. M. Chan, A. Cionca and D. V. D. Ville, “Hilbert Transform on Graphs: Let There Be Phase,” in IEEE Signal Processing Letters, doi: 10.1109/LSP.2025.3560170.
- Yeo, BT Thomas, et al. “The organization of the human cerebral cortex estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity.” Journal of neurophysiology (2011).APA